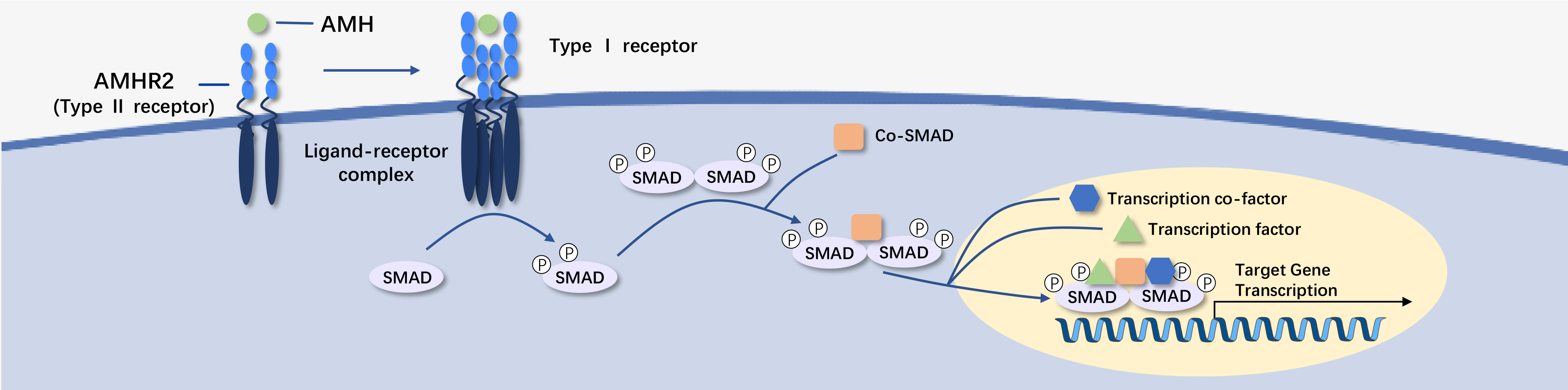
AMHR2 (anti-Müllerian hormone receptor type 2) is a protein-coding gene. This gene encodes the receptor for anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), which, in addition to testosterone, is involved in male sex differentiation. AMH and testosterone are produced by different cells in the testes and have distinct roles. Testosterone promotes the development of male reproductive organs, while the binding of AMH to its receptor prevents the Müllerian duct from developing into a uterus and fallopian tubes.
Diseases associated with AMHR2 include persistent Müllerian duct syndrome, type I and type II, as well as testicular disorders. Related pathways include ALK2 signaling events and PEDF-induced signaling. Gene ontology (GO) annotations associated with this gene involve transferase activity, transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups, and protein tyrosine kinase activity.