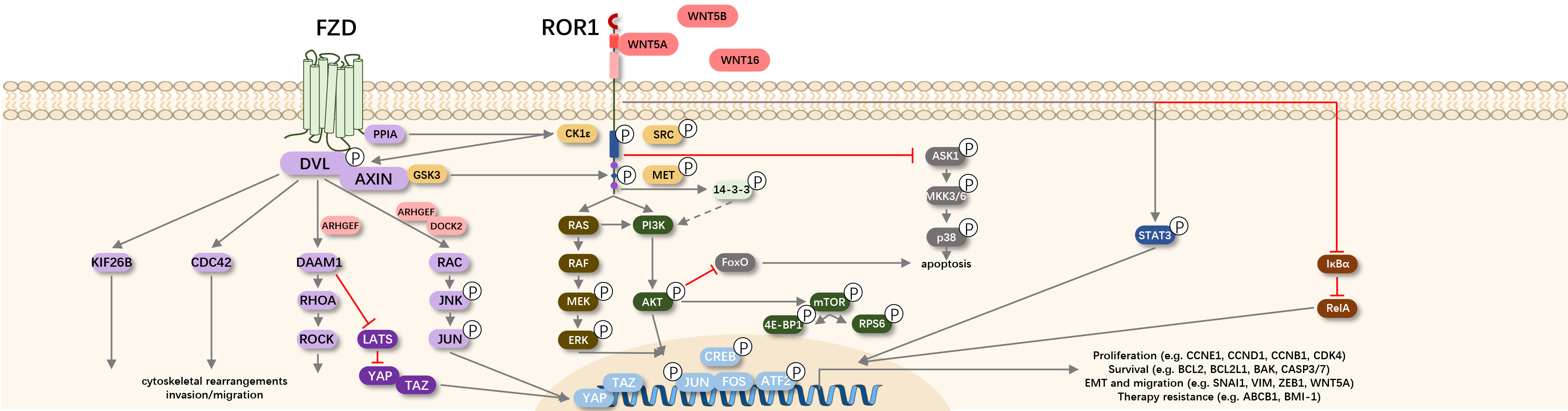
ROR1 is a receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor (ROR) family member, which is a cell surface protein. The naming of Orphan receptor is because when ROR protein was initially discovered, its ligand was unknown. However, scientists later found that ROR1 binds to the ligand Wnt5a, mediating signal transduction in non-canonical Wnt pathways, playing crucial roles in various cellular physiological processes during embryonic and infant development, including regulating cell division, proliferation, migration, and chemotaxis.
In children and adults, ROR1 expression in almost all normal tissues fades away. Nevertheless, cancer cells that revert to a dedifferentiated state can express ROR1. Blood and solid tumors expressing ROR1 possess high self-renewal potential, exhibit higher survival and migration rates, and are associated with a poor prognosis. These characteristics make this protein an ideal target for cancer therapy.