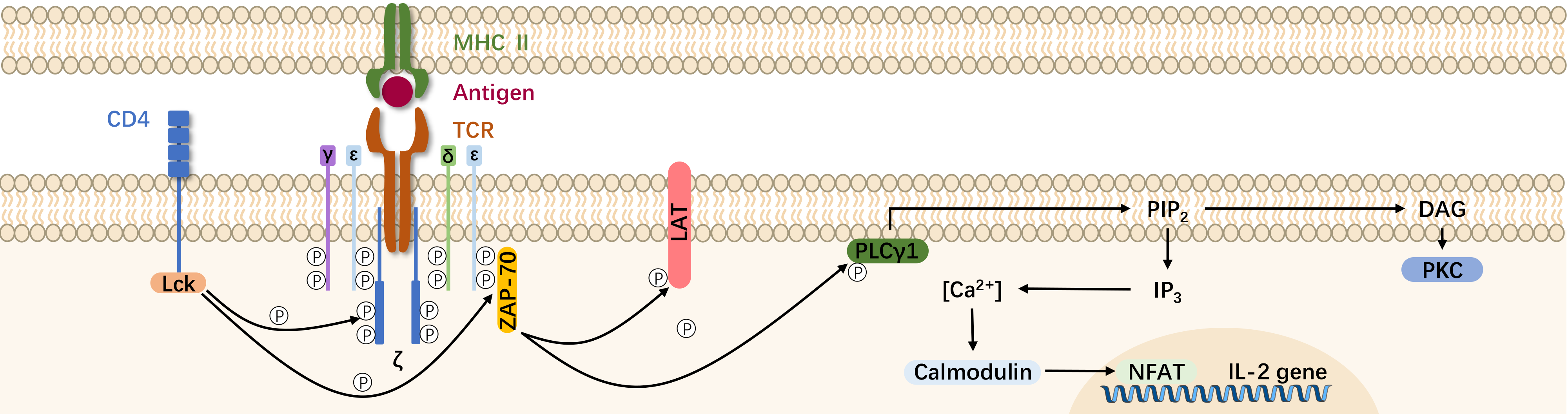
CD4+ lymphocytes are an important type of immune cells in the human immune system. The CD4 molecule is mainly expressed on helper T (Th) cells, serving as a co-receptor for antigen recognition by the Th cell TCR, binding to the non-peptide region of MHC class II molecules and participating in signal transduction for antigen recognition by Th cells. The CD4 molecule also functions as a receptor for HIV. Since the target of the AIDS virus is CD4+ cells, the detection results play a crucial role in assessing the effectiveness of AIDS treatment and the patient's immune function.