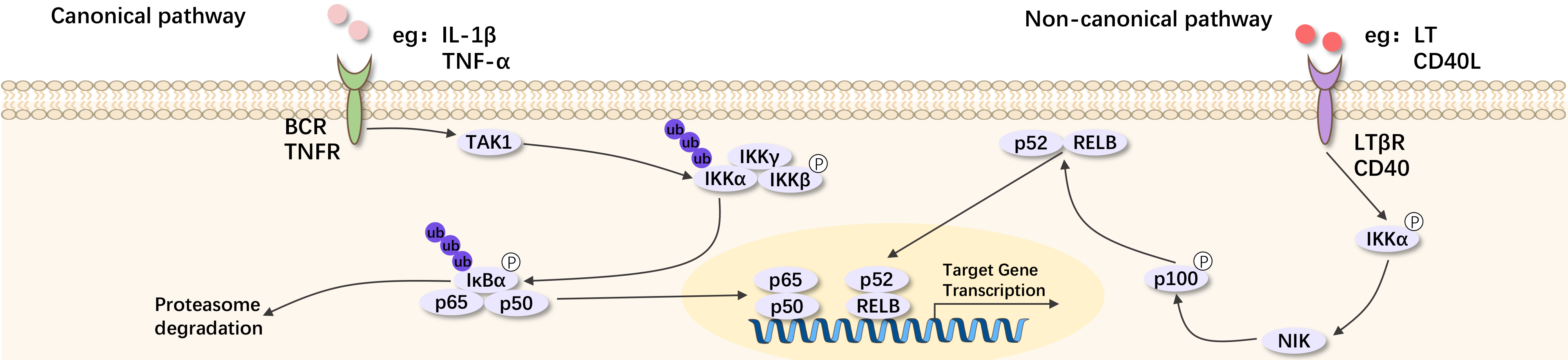
NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-κB) is an important nuclear transcription factor in cells. It is involved in the body's inflammatory response, immune response, and can regulate cell apoptosis and stress response. Overactivation of NF-κB is associated with many human diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation in heart and brain diseases. Therefore, inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway through drugs may become a means of treatment.
The N-terminal of NF-κB molecule contains a Rel homology domain, which participates in its binding to DNA and dimerization. The NF-κB inhibitory substance (IkB) can bind and inhibit NF-κB. The NF-κB molecule also contains a nuclear output domain, nuclear localization domain, translocation activation domain, and a C-terminal transactivation domain. The P50/p65 NF-κB can specifically bind to the immunoglobulin κ light chain gene transcription-enhancing sequence (κB sequence). The RelA/c-Rel dimer can bind to other sequences on target gene promoters.
The NF-κB family has 5 members, including NF-κB1 (p50), NF-κB2 (p52), RelA (p65), RelB, and c-Rel. The commonly referred NF-κB protein is the NF-κB dimer protein formed by the p65/p50 subunits and also the NF-κB2 dimer protein formed by RelB/p52 subunits.
NF-κB can be divided into two groups: the p50/p65 group, produced by the cleavage of precursors p100 and p105, p50/p52 can form dimers with other NF-κB family members and remain in the cytoplasm. The group including RelA (p65), RelB, and c-Rel do not have precursors. IkB is an inhibitory protein of NF-κB, with a molecular weight of 36kD, it can bind, inhibit NF-κB, and keep NF-κB in the cytoplasm. Tissues create the p50-p65-1eBa/p complex only in the cytoplasm. High levels of tumor necrosis factor a, phorbol esters, lipopolysaccharides, interleukin 2, H2O2, etc., can activate NF-κB-induced serine protease, then phosphorylate IκBα/β, with the phosphorylated IκBα/β lysine residues being ubiquitinated, leading to the degradation of IκBα/β, followed by the activation of p50-p65NF-κB.