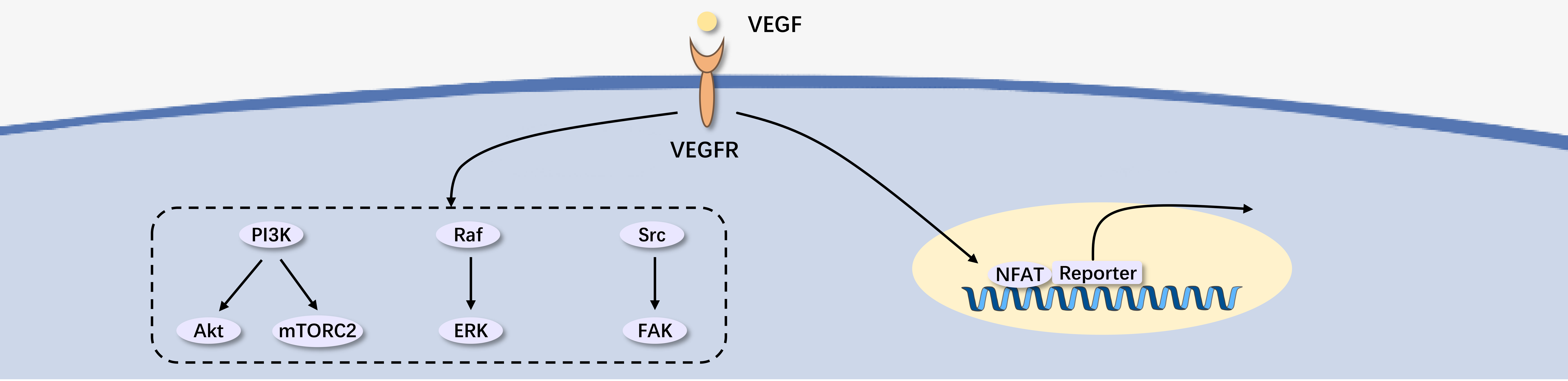
In normal physiology, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a crucial role in vascular regeneration. However, in tumor cells, angiogenic factors can activate angiogenesis, giving tumors a strong growth capability.
Among the angiogenic factors secreted by tumor cells, VEGF activates VEGF signal in endothelial cells by binding to VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases (VEGFR1/2/3), stimulating endothelial cell proliferation and survival, increasing blood vessel permeability, and maintaining tumor growth metabolism.
Anti-tumor therapies targeting the VEGF and its receptor signaling pathways are widely used, and scientists are also developing a range of combination therapies targeting VEGF and immune checkpoints.