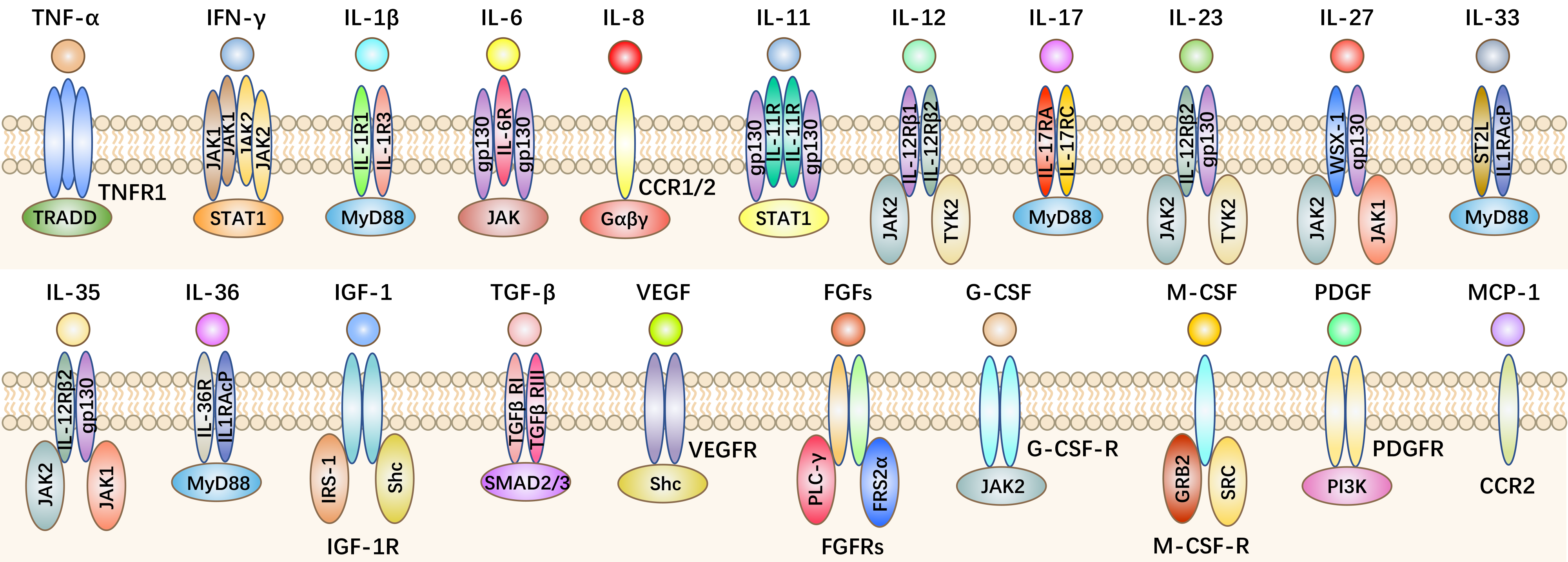
|
|
|
Anti-ACVR2B hIgG1 Antibody(Fab-17G05)
|
|
|
|
Anti-ITGB6 hIgG1 Antibody(SGN-B6A)
|
|
|
|
Anti-αvβ6 hIgG1 Antibody(m15H3)
|
|
|
|
Anti-ACVR2B hIgG1 Antibody(Bimagrumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-GARP-TGF-β1 hIgG4 Antibody(ARGX-115)
|
|
|
|
Anti-TGFB1 hIgG4 Antibody(SRK-181)
|
|
|
|
Anti-αv hIgG2 Antibody(Abituzumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-H_ACVR2B hIgG1 Reference Antibody(Bimbio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-ACVR2B mIgG2a Antibody(Bimagrumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-ACVR2A hIgG1 Antibody(LAE-102)
|
|
|
|
Anti-VEGF hIgG1 Antibody(Bevacizumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-VEGF hIgG1 Reference Antibody (Bevbio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-mouse VEGFR-2 RIgG1 Antibody(DC101)
|
|
|
|
Anti-mouse VEGFR-2 mIgG2a Antibody(DC101)
|
|
|
|
Anti-VEGFR2 hIgG1 Antibody(ramucirumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-VEGFR-1 hIgG1 Antibody (Icrucumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-H_GDF15 hIgG4 Antibody(CTL-002)
|
|
|
|
Anti-GDF15 hIgG1 Reference Antibody(Ponsbio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-H_GFRAL hIgG4 Antibody(QUEL-0301)
|
|
|
|
Anti-GDF15 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Visubio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-12/23(p40) hIgG1 antibody(Ustekinumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL7Ra hIgG1 Antibody(4A10)
|
|
|
|
Anti-H_IL-7Rα hIgG4 Antibody(lusvertikimab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-11 hIgG4 Antibody(Hu16E12)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL11 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (3C6)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-11RA hIgG1 Antibody(58B10-9C3-4E5)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL4R hIgG4 Antibody(Dupilumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-4R hIgG1 Antibody(12B5)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL4R hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Dupbio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-Mouse IL-4RA mIgG1 Antibody
|
|
|
|
Anti-ITGB3 hIgG1 Antibody(etaracizumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-CTGF hIgG1 Antibody(Pamrevlumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL31 hIgG1 Antibody(mAb33)
|
|
|
|
Anti-OSMR hIgG4 Antibody(Vixarelimab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL33 hIgG4 Antibody(Itepekimab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-CD122 hIgG1 Antibody(HuABC-2)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL5 hIgG4 Antibody(Reslizumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-5R hIgG1 Antibody(Benralizumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-CD132(IL2RG) hIgG4 Antibody(REGN7257)
|
|
|
|
Anti-CD25 hIgG1 Antibody(Basiliximab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL1R1 hIgG1 Antibody(AMG 108)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-1β hIgG1 Antibody(Canakinumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL31RA hIgG1 Antibody(NA633)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL31RA hIgG2 Antibody(Nemolizumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-17A hIgG1 Antibody(Secukinumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL17A hIgG1 Reference Antibody (Secubio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-PRLR hIgG1 Antibody(Mat3)
|
|
|
|
Anti-H_IL-22 hIgG1 Antibody(Fezakinumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-H_IL-22R1 hIgG1 Antibody(ARGX-112)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-22RA hIgG1 Reference Antibody (Temtobio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-22RA hIgG1 Antibody (280.346.TSY)
|
|
|
|
Anti-NPR1 hIgG1 Antibody(XX-16)
|
|
|
|
Anti-NPR1 hIgG4 Antibody(REGN-5381)
|
|
|
|
Anti-NPR1 hIgG1 Reference Antibody (XX-16)
|
|
|
|
Anti-NPR1 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (REGN-5381)
|
|
|
|
Anti-EphA2 hIgG1 Antibody(MEDI-547)
|
|
|
|
Anti-PRLR hIgG1 Reference Antibody(Mat3)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IGF-1R hIgG1 Antibody(teprotumumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IGF1R hIgG1 Reference Antibody(Dalobio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL33 hIgG4 ReferenceAntibody (Itepbio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-H_RANKL hIgG2 Antibody(Denosumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-23R hIgG1 Antibody(5D4)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL23A hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Risbio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL23A hIgG1 Reference Antibody (Gusebio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-mouse CD25 RIgG1 Antibody(PC-61.5.3)
|
|
|
|
Anti-mouse CD25 mIgG2a Antibody(PC-61.5.3)
|
|
|
|
Anti-GFRAL hIgG1 Antibody(NGM-120)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-9 hlgG1 Antibody(enokizumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-TPOR hIgG1 Antibody(3D9)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-12/23(p40) hIgG1 Reference Antibody(Ustebio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-GDF8 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Apitbio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-TNFSF13B(BAFF) hIgG1 Reference Antibody (Belibio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-FGFR2 hIgG1 Referece Antibody (Bemabio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-Mouse IL13 mIgG2a Antibody (BAK209B11)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL1RAP hIgG1 Antibody (Nadunolimab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL6R hIgG1 Antibody(tocilizumab)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL17A hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Ixebio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-31 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (BMS-981164)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-6 hIgG1 Reference Antibody (Siltubio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL-6 hIgG1 Reference Antibody (Clazabio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL13 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Lebribio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-IL31RA hIgG2 Reference Antibody (Nemobio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-OSMR hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Vixabio)
|
|
|
|
Anti-FGFR2 hIgG1 Antibody(hFR2-14_H12-L1)
|