Antibodies are proteins produced by the body in response to antigen stimulation, serving a protective role. These Y-shaped proteins, secreted by plasma cells (effector B cells), are utilized by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign substances like bacteria and viruses. Antibodies can recognize specific features of foreign entities, known as antigens.
The functions of antibodies in the body include:
Neutralizing toxins and preventing pathogen invasion, clearing pathogenic microorganisms;
Activating the complement system to form membrane attack complexes, leading to cell lysis and destruction by the classical pathway;
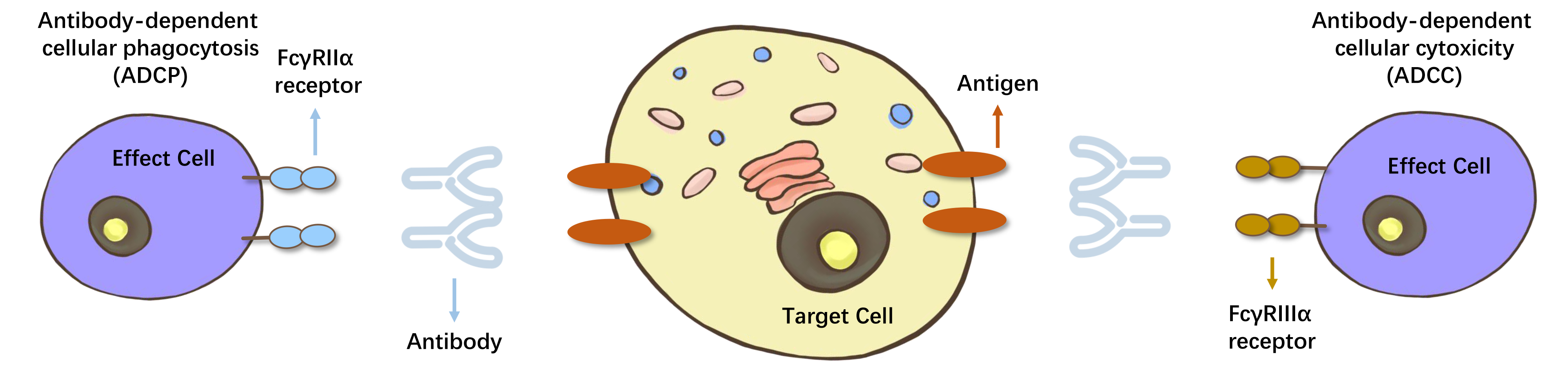
Regulating phagocytosis and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity;
Mediating type I hypersensitivity reactions;
Crossing the placental barrier and mucosal membranes, playing a crucial role in neonatal infection immunity;
Secretory IgA functioning in local mucosal immunity defense through respiratory and digestive mucosa.